What is DVMM?
DVMM (Domain-View Model Mapper) is a frontend architecture pattern for TypeScript projects. It separates backend data models (domain models) from UI models (view models) using dedicated mappers. This separation leads to cleaner code, easier maintenance, and enables backend and frontend teams to work in parallel.
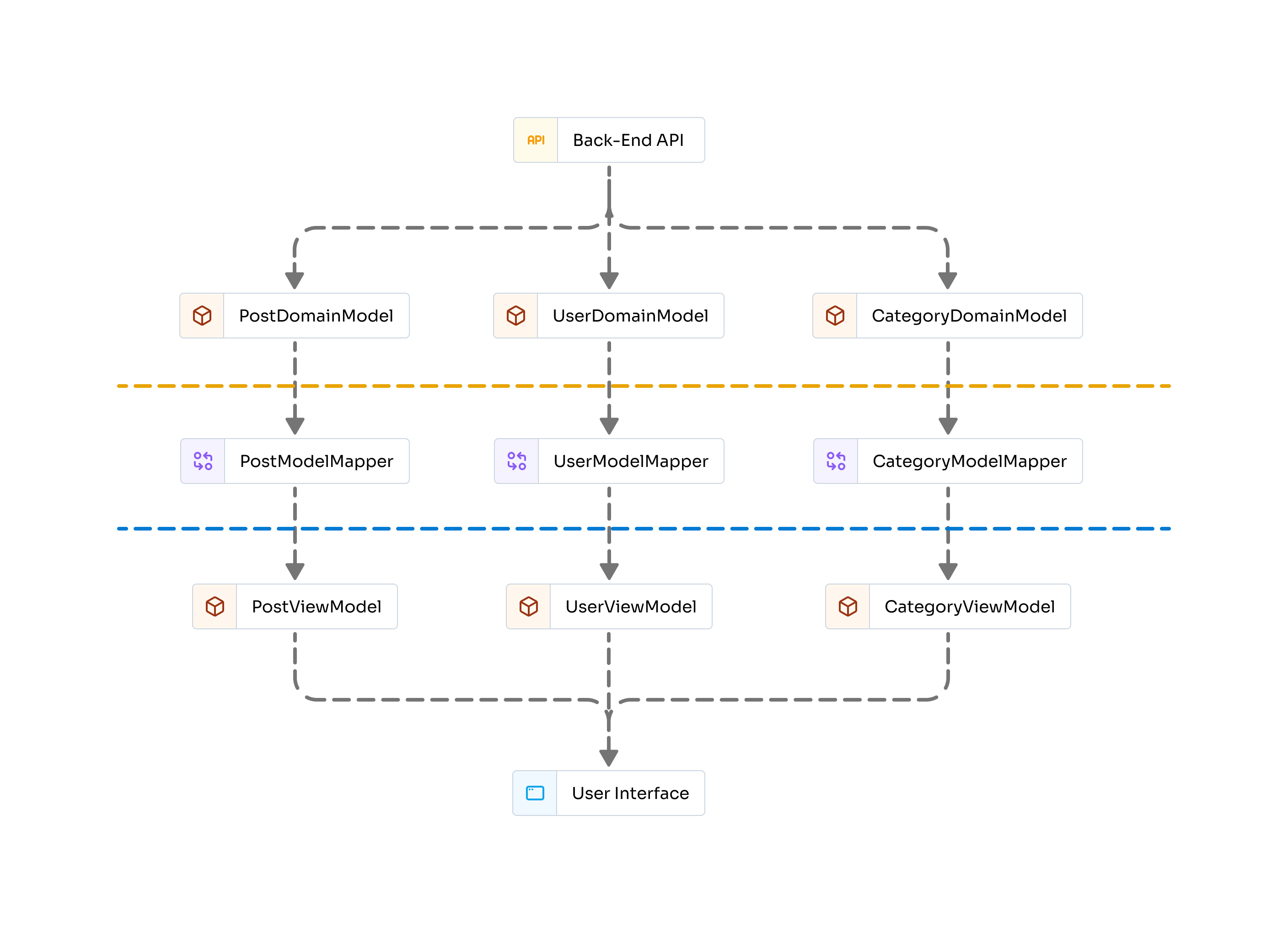
Core Concepts
Domain Model
Represents the backend API response structure. Mirrors the data contract from the server.
View Model
Represents the data structure needed by the frontend UI. Tailored for UI needs, not backend constraints.
Mapper
Contains logic to convert between domain and view models, ensuring deterministic and testable data transformations.
When to use DVMM?
DVMM is particularly useful in scenarios where the backend and frontend have different requirements or evolve at different paces. Consider adopting DVMM in the following situations:
When your backend and frontend evolve independently
In many projects, backend APIs and frontend user interfaces are developed and maintained by separate teams, often on different timelines. DVMM allows you to decouple the backend domain models from the frontend view models, so changes in the backend API (such as adding, removing, or renaming fields) do not immediately break or impact the UI. This separation enables both teams to iterate and deploy independently, reducing bottlenecks and improving overall development velocity.
When your UI needs data in a different shape than the API provides
The data structures returned by backend APIs are often optimized for storage or transport, not for direct use in the UI. With DVMM, you can define view models that are specifically tailored to the needs of your frontend components, such as grouping related fields, formatting values, or flattening nested structures. This makes it easier to render data, manage UI state, and implement features like sorting, filtering, or pagination without being constrained by the backend’s data shape.
When you want to enforce type safety and reduce bugs
By explicitly mapping between domain models and view models, DVMM ensures that data transformations are deterministic and predictable. This approach leverages TypeScript’s type system to catch mismatches and errors at compile time, reducing the likelihood of runtime bugs caused by unexpected data shapes or missing fields. Well-defined mappers also make it easier to write unit tests, further increasing the reliability and maintainability of your codebase.
When working in teams
DVMM fosters better collaboration between backend and frontend developers by clearly defining the boundaries and contracts between the two layers. Backend developers can focus on delivering robust APIs, while frontend developers can work with view models that are optimized for the UI. This parallel workflow minimizes dependencies and blockers, allowing teams to deliver features faster and with greater confidence.
Best Practices
- Keep Domain Models strictly aligned with backend.
- Shape View Models to match the UI needs, not the backend.
- Keep Mappers clean and deterministic.
- Do not use Domain Models directly in the UI.
- Use unit tests to validate mapping logic.
Summary
DVMM helps you build scalable, maintainable frontend code by clearly separating backend data contracts from UI needs. Heavily inspired by the MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel) architecture, DVMM adapts its core principles for modern TypeScript projects, emphasizing robust, testable, and future-proof applications. Use DVMM when you want to enforce clear boundaries between backend and frontend, enabling independent evolution and reliable, type-safe code.